

Artist’s Concept of a Europa lander.
As missions operate further from Earth under significant resource constraints and environmental uncertainty, autonomous technologies will have to play a greater role in their success. The goal of the OWLAT project is to facilitate the application of these technologies for NASA missions by making available the use of a testbed to physically emulate the operation of lander with a sampling tool in a low-gravity environment. The testbed comprises a lander, an instrument arm, and perception sensors typically found on lander missions. It provides the hardware interfaces and low-level software infrastructure to allow various autonomy solutions to command typical lander operations and receive telemetry and performance feedback through a ROS-based software interface in a plug-and-play manner. The project is funded by NASA Science Mission Directorate. Teams from academia and industry selected through various NASA solicitations will be using the testbed to test the performance of their autonomy algorithms.
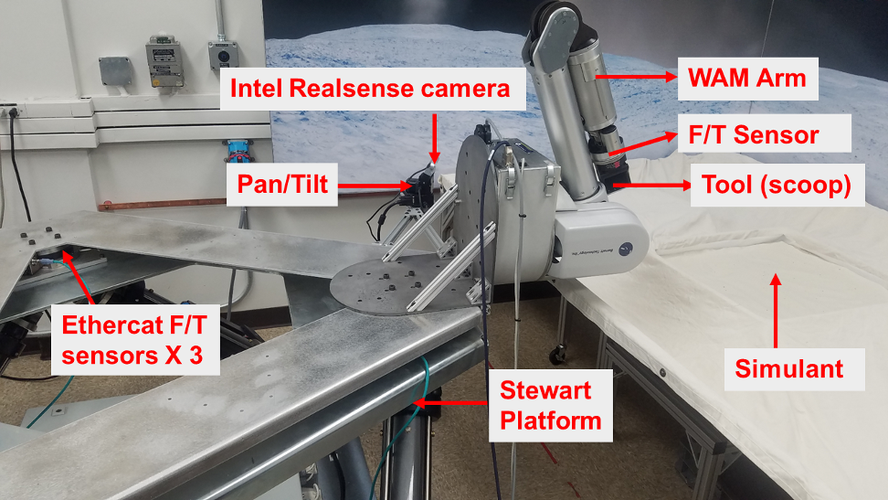
The testbed comprises a 6 DOF Stewart platform to represent the lander. A 7 DOF Barrett WAM arm represents the manipulator for carrying out surface operations. Various tools for geophysical measurements and surface sampling can be mounted interchangeably at the end of the arm. The testbed currently supports a scoop, sampling drill, pressure sinkage plate, shear bevameter and cone penetrometer instruments. A 3-axis force torque sensor is mounted between the wrist of the arm and the tool interface to provide force-torque feedback during surface operations. Three 3-axis force torque sensors are also mounted between the arm and the lander so that the reaction forces generated by the interaction of the tool with the surface can be sensed and appropriate model-based motion can then be imposed on the Stewart platform to recreate the dynamic response of the system in various low-gravity environments. An Intel RealSense stereo camera is also mounted on a pan-tilt unit for 3D perception. Various simulants can be incorporated in the simulant bin to recreate a wide variety of surface conditions.


OWLAT performing pressure-sinkage test (top), and scooping operation (bottom).